Stanford NLP 关于关系抽取的笔记,仅探讨如何提取关系的三元组(triple),即一个谓词(predicate)带 2 个形参(argument),比如说 Founding-location(IBM,New York) 这类。
关系抽取的应用领域还是很广泛的,如
- 建立新的结构化的知识库(knowledge bases)
几乎各个领域都会用到 - 扩大现有知识库
将更多的单词添加到 WordNet 词典(thesaurus)
将更多事实(facts) 添加到 FreeBase 或者 DBPedia中 - 支持 QA 系统
The granddaughter of which actor starred in the movie “E.T.”?
(acted-in ?x “E.T.”)(is-a ?y actor)(granddaughter-of ?x ?y)
先来看下关系抽取的数据集以及现有的关系定义。比较有名的ACE(Automated Content Extraction)有 6 大类关系 17 个子类,用于医疗的UMLS 有 134 中 entity type,54 种关系……
还有的一些世界范围内知名的高质量大规模开放知识图谱,如包括 DBpedia、Yago、Wikidata、BabelNet、ConceptNet 以及 Microsoft Concept Graph等,中文的有开放知识图谱平台 OpenKG……
ACE 的 17 类关系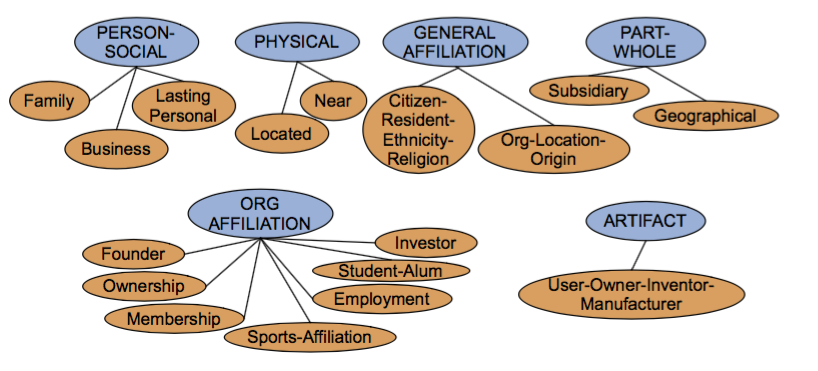
具体的应用实例
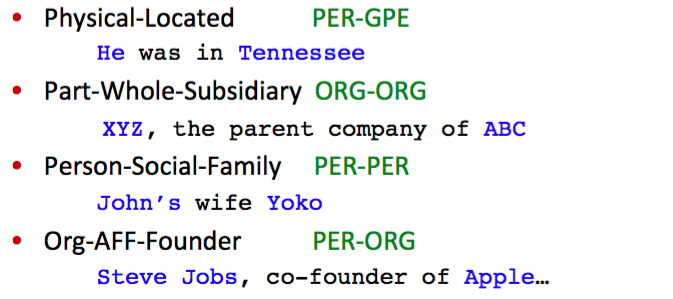
Wikipedia 的 info box
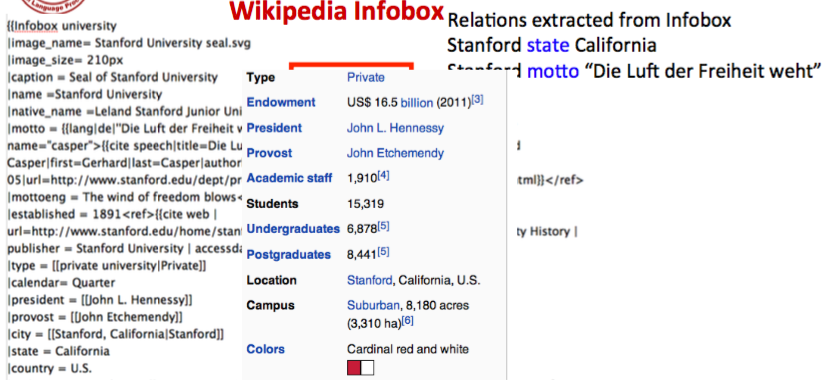
info box 信息可以转换成 RDF 三元组 $(subject \ predicate \ object)$ 如
|
|
常用的 Freebase relations
|
|
RDF 是一种本体语言,关于本体,貌似是本科时的东西了,就不多说了。
Relation extractors
- 手写规则(hand-written patterns)
- 监督学习(supervised machine learning)
- 半监督/无监督学习(semi-supervised and unsupervised)
- Bootstrapping(using seeds)
- Distant supervision
- Unsupervised learning from the web
Hand-written patterns
首先是基于字符串的 pattern,举一个 IS-A 的关系
Agar is a substance prepared from a mixture of red algae, such as Gelidium, for laboratory or industrial use
通过 such as 可以判断这是一种 IS-A 的关系,可以写的规则是:
|
|
另一个直觉是,更多的关系是在特定是实体之间的,所以我们可以用 Named entity tag 来帮助关系抽取,比如说
|
|
然后想到了我们可以把基于字符串的 pattern 和基于 ner 的 pattern 结合起来,就有了下面的例子。

对应的工具有 Stanford CoreNLP 的 tokensRegex。
手写规则的优点是:
- 人工规则有高准确率(high-precision)
- 可以为特定领域定制(tailor)
缺点是:
- 低召回率(low-recall)
- 要考虑周全所有可能的 pattern 很难,也很费时间精力
- 需要为每条关系来定义 pattern
Supervised relation extraction
研究综述
漆桂林,高桓,吴天星.知识图谱研究进展[J].情报工程,2017,3(1):004-025
Zhou[13] 在 Kambhatla 的基础上加入了基本词组块信息和 WordNet,使用 SVM 作为分类器,在实体关系识别的准确率达到了 55.5%,实验表明实体类别信息的特征有助于提高关系抽取性能; Zelenko[14] 等人使用浅层句法分析树上最小公共子树来表达关系实例,计算两颗子树之间的核函数,通过训练例如 SVM 模型的分类器来对实例进行分。但基于核函数的方法的问题是召回率普遍较低,这是由于相似度计算过程匹配约束比较严格,因此在后续研究对基于核函数改进中,大部分是围绕改进召回率。但随着时间的推移,语料的增多、深度学习在图像和语音领域获得成功,信息抽取逐渐转向了基于神经模型的研究,相关的语料被提出作为测试标准,如 SemEval-2010 task 8[15]。基于神经网络方法的研究有,Hashimoto[16] 等人利用 Word Embedding 方法从标注语料中学习特定的名词对的上下文特征,然后将该特征加入到神经网络分类器中,在 SemEval-2010 task 8 上取得了 F1 值 82.8% 的效果。基于神经网络模型显著的特点是不需要加入太多的特征,一般可用的特征有词向量、位置等,因此有人提出利用基于联合抽取模型,这种模型可以同时抽取实体和其之间的关系。联合抽取模型的优点是可以避免流水线模型存在的错误累积[17-22]。其中比较有代表性的工作是[20],该方法通过提出全新的全局特征作为算法的软约束,进而同时提高关系抽取和实体抽取的准确率,该方法在 ACE 语料上比传统的流水线方法 F1 提高了 1.5%,;另一项工作是 [22],利用双层的 LSTM-RNN 模型训练分类模型,第一层 LSTM 输入的是词向量、位置特征和词性来识别实体的类型。训练得到的 LSTM 中隐藏层的分布式表达和实体的分类标签信息作为第二层 RNN 模型的输入,第二层的输入实体之间的依存路径,第二层训练对关系的分类,通过神经网络同时优化 LSTM 和 RNN 的模型参数,实验与另一个采用神经网络的联合抽取模型[21]相比在关系分类上有一定的提升。但无论是流水线方法还是联合抽取方法,都属于有监督学习,因此需要大量的训练语料,尤其是对基于神经网络的方法,需要大量的语料进行模型训练,因此这些方法都不适用于构建大规模的 Knowledge Base。
[13] Guodong Z, Jian S, Jie Z, et al. ExploringVarious Knowledge in relation Extraction.[c]// acl2005, Meeting of the Association for ComputationalLinguistics, Proceedings of the Conference, 25-30 June, 2005, University of Michigan, USA. DBLP.2005:419-444.
[14] Zelenko D, Aone C, Richardella A. KernelMethods for relation Extraction[J]. the Journal ofMachine Learning Research, 2003, 1083-1106.
[15] Hendrickx I, Kim S N, Kozareva Z, et al.semEval-2010 task 8: Multi-way classification ofsemantic relations between Pairs of nominals[c]//the Workshop on semantic Evaluations: recentachievements and Future Directions. association forComputational Linguistics, 2009:94-99.
[16] Hashimoto K, Stenetorp P, Miwa M, et al. Task-oriented learning of Word Embeddings for semanticRelation Classification[J], Computer Science,2015:268-278.
[17] Singh S, Riedel S, Martin B, et al. JointInference of Entities, Relations, and Coreference[C]//the Workshop on automated Knowledge baseConstruction ,San Francisco, CA, USA, October27-november 1. 2013:1-6.
[18] Miwa M, Sasaki Y. Modeling Joint Entity andrelation Extraction with table representation[c]//conference on Empirical Methods in naturalLanguage Processing. 2014:944-948.
[19] Lu W, Dan R. Joint Mention Extraction andclassification with Mention Hypergraphs[c]//conference on Empirical Methods in naturallanguage Processing. 2015:857-867.
[20] Li Q, Ji H. Incremental Joint Extraction of EntityMentions and relations[c]// annual Meeting of theAssociation for Computational Linguistics. 2014:402-412.
[21] Kate R J, Mooney R J. Joint Entity andrelation Extraction using card-pyramid Parsing[c]//conference on computational natural languagelearning. 2010:203-212.
[22] Miwa M, Bansal M. End-to-End Relation Extraction using lstMs on sequences and tree structures[c]// annual Meeting of the association for computational linguistics. 2016:1105-1116.
分类器
非常传统的监督学习思路
|
|
为了提高 efficiency,通常我们会训练两个分类器,第一个分类器是 yes/no 的二分类,判断命名实体间是否有关系,如果有关系,再送到第二个分类器,给实体分配关系类别。这样做的好处是通过排除大多数的实体对来加快分类器的训练过程,另一方面,对每个任务可以使用 task-specific feature-set。
可以采用的分类器有
- MaxEnt
- Naive Bayes
- SVM
- …
特征
E.g., American Airlines, a unit of AMR, immediately matched the move, spokesman Tim Wagner said
Mention 1: American Airlines
Mention 2: Tim Wagner
Word features
- Headwords of M1 and M2, and combination
- M1: Airlines, M2: Wagner, Combination: Airlines-Wagner
- Bag of words and bigrams in M1 and M2
- {American, Airlines, Tim, Wagner, American Airlines, Tim Wagner}
- Words or bigrams in particular positions left and right of M1/M2
- M2: -1 spokesman
- M2: +1 said
- Bag of words or bigrams between the two entities
- {a, AMR, of, immediately, matched, move, spokesman, the, unit}
Named Entities Type and Mention Level Features
- Named-entities types
M1: ORG
M2: PERSON - Concatenation of the two named-entities types
ORG-PERSON - Entity Level of M1 and M2 (NAME, NOMINAL, PRONOUN)
M1: NAME [it or he would be PRONOUN]
M2: NAME [the company would be NOMINAL]
Parse Features
- Base syntactic chunk sequence from one to the other
NP NP PP VP NP NP - Constituent path through the tree from one to the other
NP ↑ NP ↑ S ↑ S ↓ NP - Dependency path
Airlines matched Wagner said
Gazetteer and trigger word features
- Trigger list for family: kinship terms
parent, wife, husband, grandparent, etc. [from WordNet] - Gazetteer:
List of useful geo or geopolitical words
Country name list
Other sub-entities

Evaluation
最常用的 Precision, Recall, F1

小结
如果测试集和训练集很相似,那么监督学习的准确率会很高,然而,它对不同 genre 的泛化能力有限,模型比较脆弱,另一方面,获取这么大的训练集代价也是昂贵的。
Semi-supervised realation extraction
Seed-based or bootstrapping approaches
半监督学习主要是利用少量的标注信息进行学习,这方面的工作主要是基于 Bootstrap 的方法。基于 Bootstrap 的方法主要是利用少量的实例作为初始种子(seed tuples)的集合,然后利用 pattern 学习方法进行学习,通过不断的迭代,从非结构化数据中抽取实例,然后从新学到的实例中学习新的 pattern 并扩充 pattern 集合。
漆桂林,高桓,吴天星.知识图谱研究进展[J].情报工程,2017,3(1):004-025
Brin[23]等人通过少量的实例学习种子模板,从网络上大量非结构化文本中抽取新的实例,同时学习新的抽取模板,其主要贡献是构建了 DIPRE 系统;Agichtein[24]在 Brin 的基础上对新抽取的实例进行可信度的评分和完善关系描述的模式,设计实现了 Snowball 抽取系统;此后的一些系统都沿着 Bootstrap 的方法,但会加入更合理的对 pattern 描述、更加合理的限制条件和评分策略,或者基于先前系统抽取结果上构建大规模 pattern;如 NELL(Never-EndingLanguage Learner)系统[25-26],NELL 初始化一个本体和种子 pattern,从大规模的 Web 文本中学习,通过对学习到的内容进行打分来提高准确率,目前已经获得了 280 万个事实。
[23] brin s. Extracting Patterns and relations fromthe World Wide Web[J]. lecture notes in computerScience, 1998, 1590:172-183.
[24] Agichtein E, Gravano L. Snowball : Extractingrelations from large Plain-text collections[c]// acMConference on Digital Libraries. ACM, 2000:85-94.
[25] Carlson A, Betteridge J, Kisiel B, et al. Toward anarchitecture for never-Ending language learning.[c]// twenty-Fourth aaai conference on artificialIntelligence, AAAI 2010, Atlanta, Georgia, Usa, July.DBLP, 2010:529-573.
[26] Mitchell T, Fredkin E. Never-ending Languagelearning[M]// never-Ending language learning.Alphascript Publishing, 2014.
Relation Bootstrapping
|
|
看一个完整的例子

从 5 对种子开始,找到包含种子的实例,替换关键词,形成 pattern,迭代匹配,就为 $(authoer, book)$ 抽取到了 relation pattern,x, by y, 和 x, one of y’s
Snowball
对 Dipre 算法的改进。Snowball 也是一种相似的迭代算法,Dipre 的 X,Y 可以是任何字符串,而 Snowball 要求 X,Y 必须是命名实体,并且 Snowball 对每个 pattern 计算了 confidence value
|
|
Distant Supervision
Distant Supervision 其实结合了 bootstrapping 和监督学习的长处,它使用一个大的数据库来得到海量的 seed example,然后从这些 example 中创建许多的 feature,最后与有监督的分类器相结合。
与监督学习相似的是这种方法用许多的 feature 训练了一个分类器,通过详细的人工创造的知识进行监督,不需要用迭代的方法来扩充 pattern。
与无监督学习相似的是这种方法采用了大量没有标注的数据,对训练语料库中的 genre 并不敏感,适合泛化。
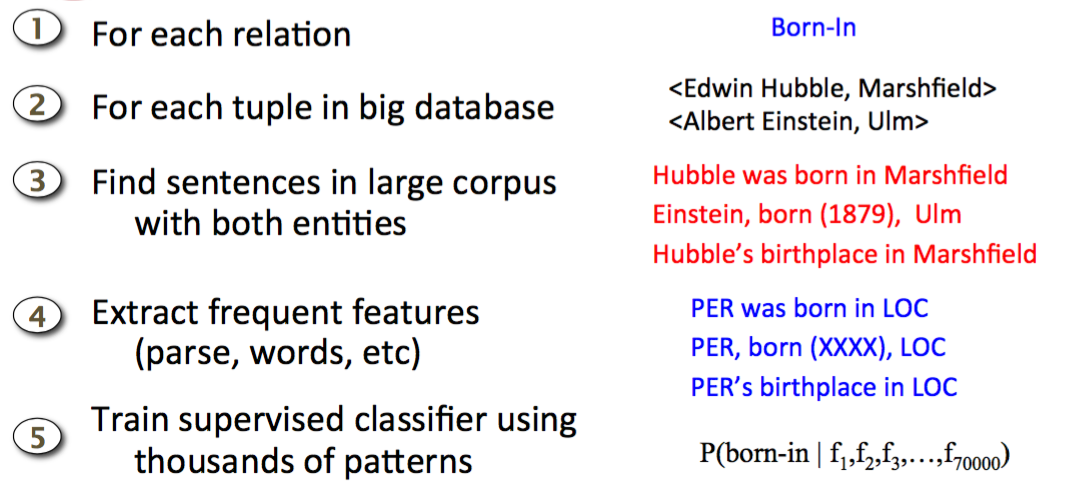
Unsupervised relation extraction
Bollegala[27]从搜索引擎摘要中获取和聚合抽取模板,将模板聚类后发现由实体对代表的隐含语义关系; Bollegala[28]使用联合聚类(Co-clustering)算法,利用关系实例和关系模板的对偶性,提高了关系模板聚类效果,同时使用 L1 正则化 Logistics 回归模型,在关系模板聚类结果中筛选出代表性的抽取模板,使得关系抽取在准确率和召回率上都有所提高。
无监督学习一般利用语料中存在的大量冗余信息做聚类,在聚类结果的基础上给定关系,但由于聚类方法本身就存在难以描述关系和低频实例召回率低的问题,因此无监督学习一般难以得很好的抽取效果。
[27] Bollegala D T, Matsuo Y, Ishizuka M. Measuringthe similarity between implicit semantic relationsfrom the Web[J]. Www Madrid! track semantic/dataWeb, 2009:651-660.
[28] Bollegala D T, Matsuo Y, Ishizuka M. RelationalDuality: Unsupervised Extraction of semantic relations between Entities on the Web[c]//International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW 2010, Raleigh, North Carolina, Usa, April. DBLP, 2010:151-160.
Open Information Extraction 从网络中抽取关系,没有训练数据,没有关系列表。过程如下:
Evaluation of Semi-supervised and Unsupervised Relation Extraction
因为抽取的是新的关系,并不能准确的计算 precision 和 recall。然而我们可以估计,从结果集中随机抽取一个关系的 sample,然后人工来检验准确率
$$\hat P = {\text {Number of correctly extracted relations in the sample} \over \text {Total number of extracted relations in the sample}}$$
也可以计算不同 recall level 上的 precision,比如说分别计算在前 1000,10,000,100,000 个新的关系中的 precision,在各个情况下随机取样。
然而,并没有方法来计算 recall。

